And amid this. Mushrooms are high in Vitamins D and B boost immunity level contain cancer-fighting properties aid in lowering cholesterol fight against ageing and have anti-inflammatory powers.
Vitamin D has several important functions.
Vit d for immunity. Deficiency in vitamin D is associated with increased autoimmunity and an increased susceptibility to infection. Heres the big reason why vitamin D can. Researchers found it also affects key cells of the immune system.
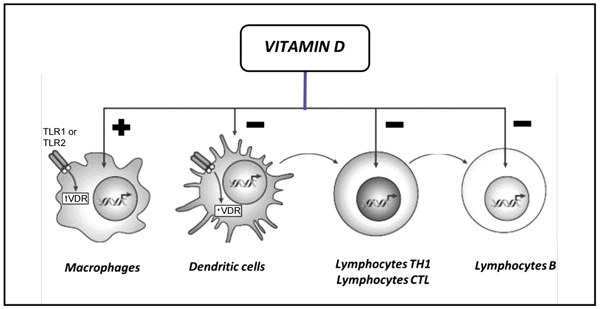
Vitamin D can modulate the innate and adaptive immune responses. It inhibits B cell proliferation and blocks B cell differentiation and immunoglobulin secretion31-32. Vitamin D can do a slew of different things in your body including strengthen your bones reduce inflammation and help with immune function the NIH says.
New studies conclude that vitamin D can reduce your risk of developing COVID-19 as well as decrease the severity of the illness. Vitamin D is produced by the body in response to sunlight and is often lauded for its health benefits. Autoimmune diseases result from an aberrant activation of the immune system whereby the immune response is directed against harmless self-antigens.
As immune cells in autoimmune diseases are responsive to the ameliorative effects of vitamin D the beneficial effects of supplementing vitamin D-deficient individuals with autoimmune disease. How eggs and chickens contribute to Vitamin D supplements in our body. This discovery might explain.
Perhaps the most vital are regulating the absorption of calcium and phosphorus and facilitating normal immune system function. However vitamin D performs various immunomodulatory anti-inflammatory antioxidant and anti-fibrotic actions. Two key factors have underpinned this revised perspective.
It also helps regulate the calcium and phosphate in our body which in turn strengthens the bones and muscles. Vitamin D additionally suppresses T cell proliferation and results in a shift from a Th1 to a Th2 phenotype34-35. Scientists have found that vitamin D is crucial to activating our immune defenses and that without sufficient intake of the vitamin - the killer cells of the immune system -- T cells --.
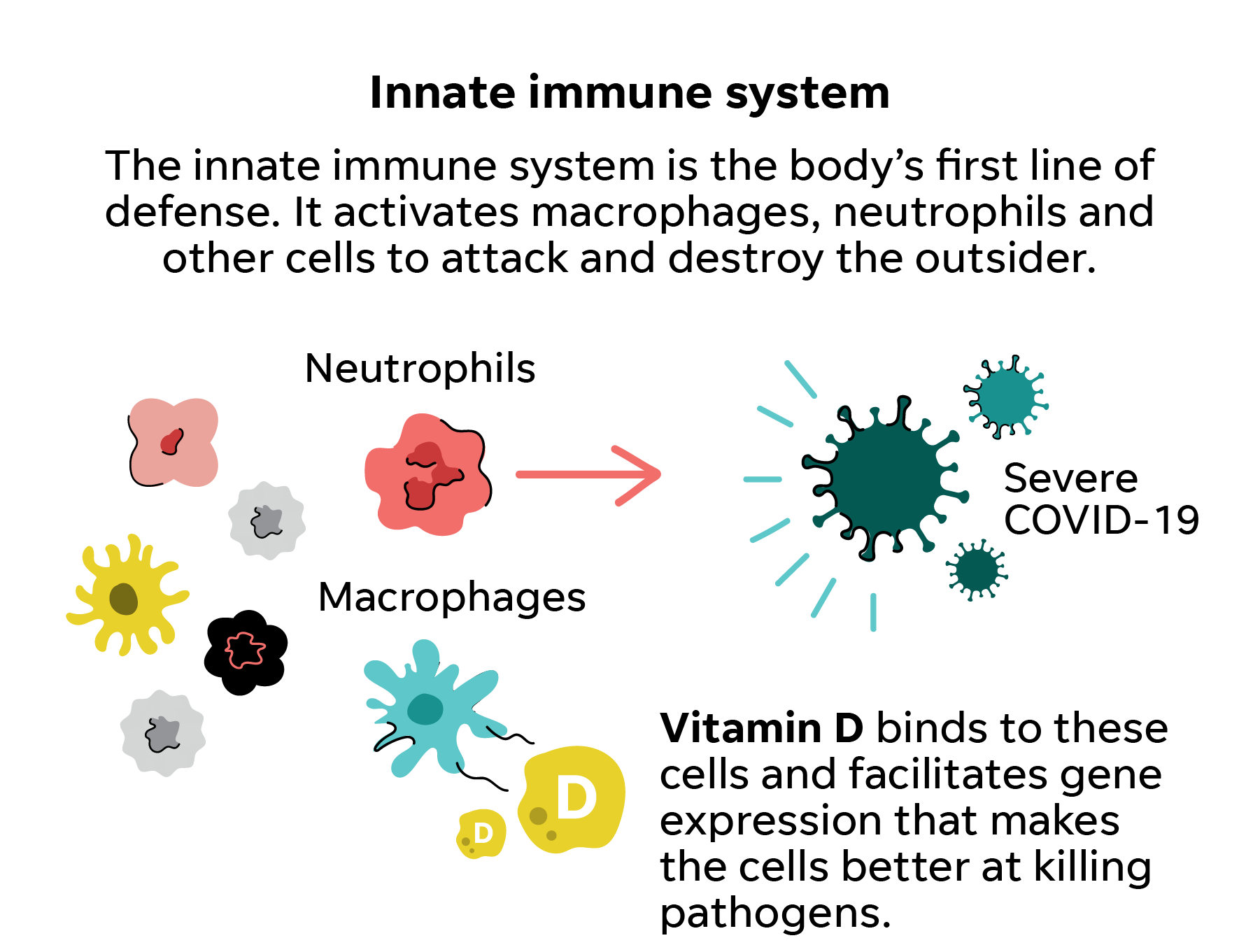
Vitamin D is critical for bone and mineral metabolism. Because the vitamin D receptor is expressed on immune cells such as B cells T cells and antigen-presenting cells and because these cells can synthesize the active vitamin D metabolite vitamin D also has the potential to modulate innate and adaptive immune responses. In the first instance vitamin D prompts a strong antibacterial response from the innate immune system our first line of defence to kill pathogensIf this fails our adaptive immune system the.
Vitamin D metabolizing enzymes and vitamin D receptors are present in many cell types including various immune cells such as antigen-presenting-cells T cells B cells and monocytes. Vitamin D and immune health Research shows that vitamin D plays an important role in immune function and a deficiency in it is shown to increase your susceptibility to infection. Low levels of vitamin D have also been associated with frequent infections.
Experts say vitamin D boosts the immune system which can help fight. In 2009 the National Institute of Health warned that low vitamin D levels are associated with frequent colds and influenza. Vitamin D has both anti-inflammatory and immune regulatory properties and is crucial for the activation of immune system defenses.
In vitro data show that in addition to modulating innate immune cells vitamin D also promotes a more tolerogenic immunological status. And so it appears that vitamin D helps keep the immune system balanced much like a gymnast walking on a balance beam. Immunomodulatory actions of vitamin D have been recognised for over a quarter of a century but it is only in the last few years that the significance of this to normal human physiology has become apparent.
Vitamin D has numerous effects on cells within the immune system.