Surfactant is a natural substance that lowers surface tension in your lungs and allows you to breathe. Surfactant is a macromolecular complex largely composed of phospholipids 8085 mainly phosphatidylcholine of which dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine is the major surface-active.
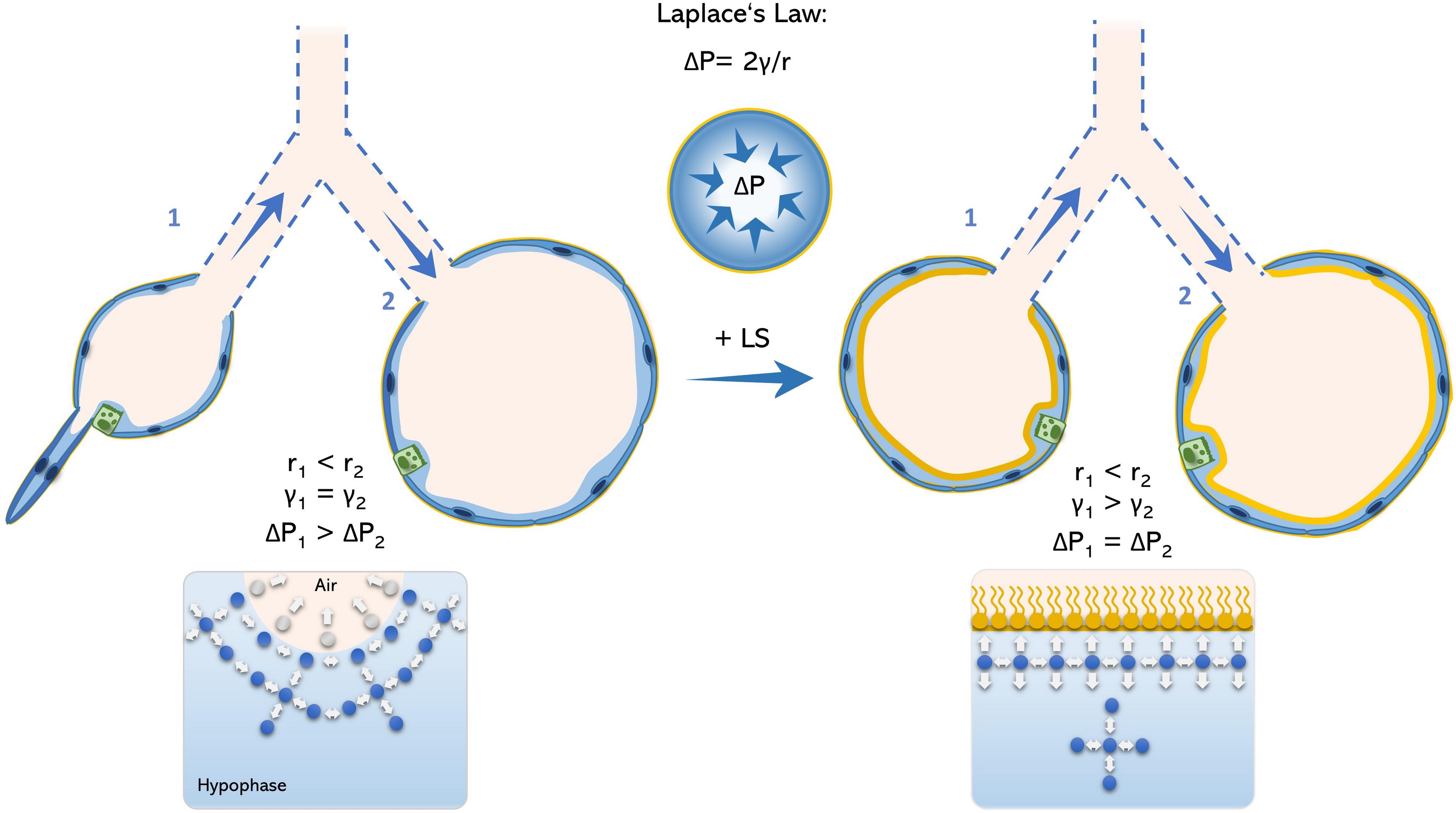 Frontiers Alveolar Dynamics And Beyond The Importance Of Surfactant Protein C And Cholesterol In Lung Homeostasis And Fibrosis Physiology
Frontiers Alveolar Dynamics And Beyond The Importance Of Surfactant Protein C And Cholesterol In Lung Homeostasis And Fibrosis Physiology
The substance is composed of phospholipids and four surfactant proteins known as hydrophilic proteins SP-A and SP-D and hydrophobic proteins SP-B and SP-C.
What is surfactant in lungs. This allows surfactant to serve three functions in the respiratory system. PAP causes mild to severe. Pulmonary surfactant is a complex and highly.
It is produced in fetal lungs and begins working as soon as the baby has reached full term and is delivered. A surface-active agent including substances commonly referred to as wetting agents surface tension depressants. Pulmonary surfactant is a complex and highly surface active material composed of lipids and proteins which is found in the fluid lining the alveolar surface of the lungs.
Summary Pulmonary surfactant is a complex mixture of specific lipids proteins and carbohydrates which is produced in the lungs by type II alveolar epithelial cells. 59k views Reviewed 2 years ago. Surfactant keeps your lungs from collapsing effectively defying the laws of surface physics to allow your air spaces to remain open and bring gas to and from your blood.
Surfactant that lines the epithelium of the alveoli in lungs is known as pulmonary surfactant and it decreases the surface tension on the alveolar membrane. The three main types of PAP are congenital acquired and secondary. The mixture is surface active and acts to decrease surface tension at the airliquid interface of the alveoli.
Surfactant contributes to the elastic properties of pulmonary tissue preventing the alveoli from collapsing. Surfactant is enriched with a relatively unique phospholipid termed dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine and four surfactant-associated proteins SP-A SP-B SP-C and SP-D. The underlying Young-Laplace equation applying to the surface of any geometrical structure is.
Surfactant is a surface acting material or agent that is responsible for lowering the surface tension of a fluid. Surfactant is a complex substance that prevents the collapse of alveoli in the lungs. Reduction of surface tension Maintaining alveolar stability Reduction of ultra-filtration hence pulmonary oedema.
Pulmonary surfactant makes it easier for people to breathe by reducing surface tension in the lungs. Its specific function is to reduce surface tension at the pulmonary air-liquid interface. Surfactant prevents alveolar collapse at low lung volume and preserves bronchiolar patency during normal and forced respiration.
Without this substance in the lungs people would have trouble breathing and their breathing would be much noisier. Pulmonary surfactant A lipoprotein secreted by type II alveolar cells that decreases the surface tension of the fluid lining the alveoli permitting expansion. The term is also used in the medical community to refer specifically to a substance secreted by the cells that line the lungs.
Pulmonary surfactant is essential for life as it lines the alveoli to lower surface tension thereby preventing atelectasis during breathing. Synthetic lung surfactant is available for treating patients with respiratory distress syndrome. Pulmonary surfactant is responsible for reducing surface tension at the airliquid interface in the alveoli preventing lung collapse at resting lung pressures.
Those surface-active agents forming a monomolecular layer over pulmonary alveolar surfaces. A fluid secreted by the cells of the alveoli the tiny air sacs in the lungs that serves to reduce the surface tension of pulmonary fluids. CONTINUE SCROLLING OR CLICK HERE.
Surfactants are natural complexes of phospholipids and proteins that are present at the airliquid interface of the lungs to lower surface tension. Replacement with exogenous surfactant in preterm infants is one of the most significant advances in neonatology. Lung surfactant is a complex with a unique phospholipid and protein composition.
 Purdue Startup Developing Novel Treatment For Life Threatening Lung Condition Taking Part In Prominent Accelerator Program Purdue University News
Purdue Startup Developing Novel Treatment For Life Threatening Lung Condition Taking Part In Prominent Accelerator Program Purdue University News
Biophysical Study Of Lung Surfactant Laboratory Of Biocolloids And Biointerfaces
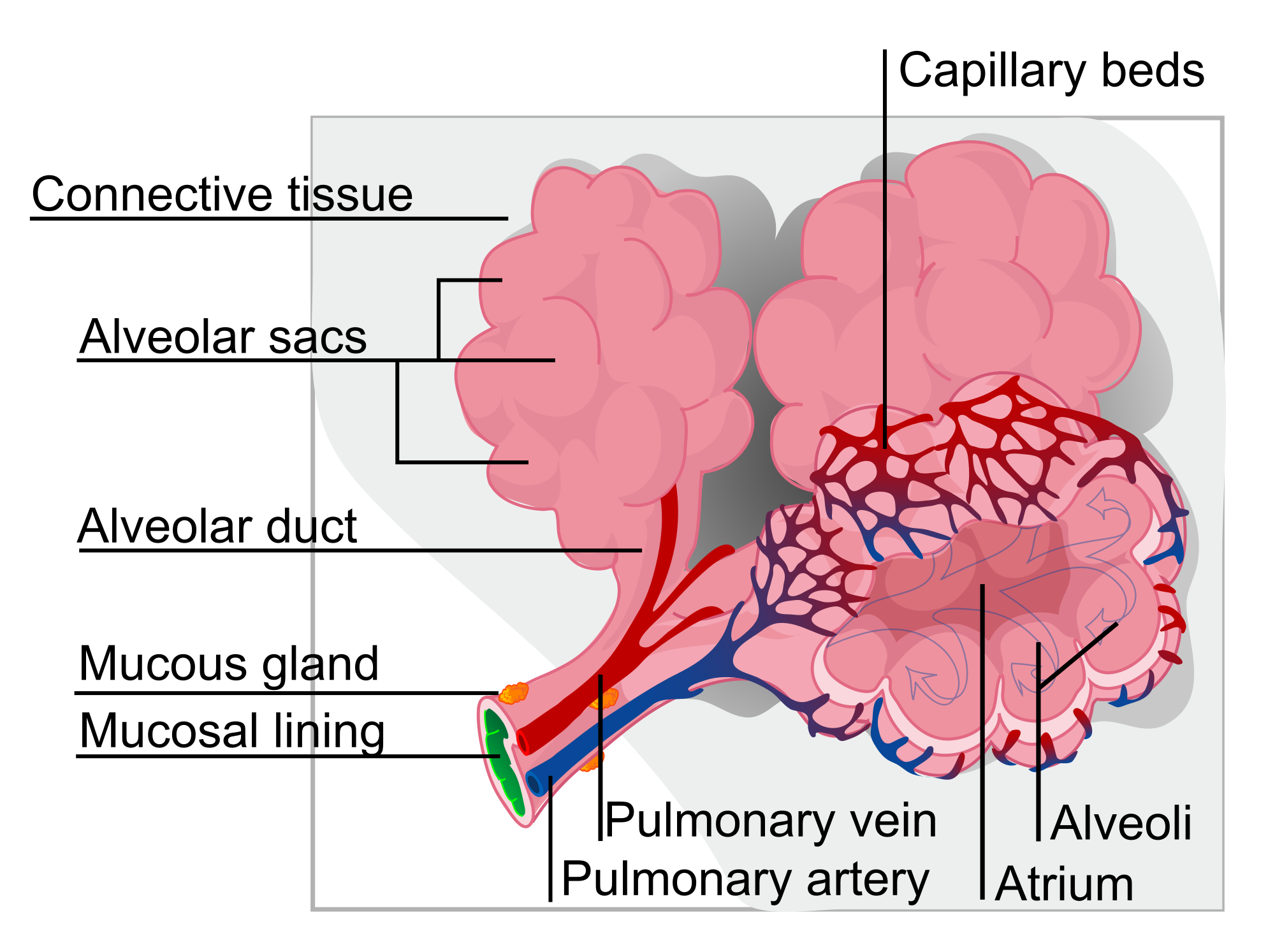 Pulmonary Surfactant Wikipedia
Pulmonary Surfactant Wikipedia
 Pulmonary Surfactant Inhibition Of Nanoparticle Uptake By Alveolar Epithelial Cells Scientific Reports
Pulmonary Surfactant Inhibition Of Nanoparticle Uptake By Alveolar Epithelial Cells Scientific Reports
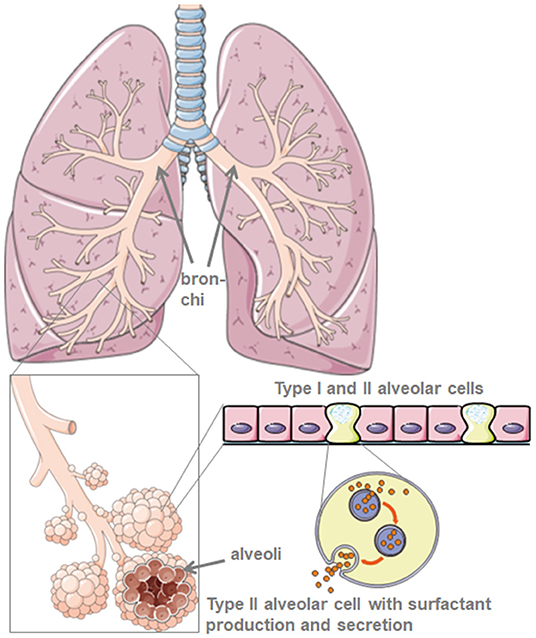 Frontiers Lung Surfactant For Pulmonary Barrier Restoration In Patients With Covid 19 Pneumonia Medicine
Frontiers Lung Surfactant For Pulmonary Barrier Restoration In Patients With Covid 19 Pneumonia Medicine
 Interactions Of Particulate Matter And Pulmonary Surfactant Implications For Human Health Sciencedirect
Interactions Of Particulate Matter And Pulmonary Surfactant Implications For Human Health Sciencedirect
Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis Pap
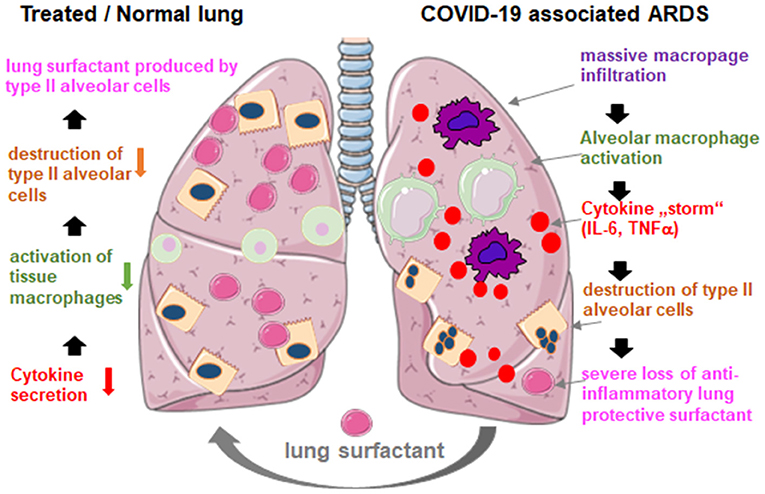 Frontiers Lung Surfactant For Pulmonary Barrier Restoration In Patients With Covid 19 Pneumonia Medicine
Frontiers Lung Surfactant For Pulmonary Barrier Restoration In Patients With Covid 19 Pneumonia Medicine
 Regulation Of Surfactant Secretion In Alveolar Type Ii Cells American Journal Of Physiology Lung Cellular And Molecular Physiology
Regulation Of Surfactant Secretion In Alveolar Type Ii Cells American Journal Of Physiology Lung Cellular And Molecular Physiology
 Understanding The Principle Biophysics Concepts Of Pulmonary Surfactant In Health And Disease Adc Fetal Neonatal Edition
Understanding The Principle Biophysics Concepts Of Pulmonary Surfactant In Health And Disease Adc Fetal Neonatal Edition
Biophysical Study Of Lung Surfactant Laboratory Of Biocolloids And Biointerfaces
 Jci Pulmonary Surfactant A Front Line Of Lung Host Defense
Jci Pulmonary Surfactant A Front Line Of Lung Host Defense
 Pulmonary Surfactant In Newborn Infants And Children European Respiratory Society
Pulmonary Surfactant In Newborn Infants And Children European Respiratory Society
 Pulmonary Surfactant Biomimetic Nanoparticles Potentiate Heterosubtypic Influenza Immunity Science
Pulmonary Surfactant Biomimetic Nanoparticles Potentiate Heterosubtypic Influenza Immunity Science

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.