Early vaccines used inoculation of a similar but harmless pathogen to develop immunity to deadly pathogens. These elements of vaccines and other molecules and micro-organisms that stimulate the immune system are called antigens Babies are exposed to thousands of germs and other antigens in the environment from the time they are born.
Mrna Vaccines Covid 19 Biontech
However vaccination is safer than natural infection because it doesnt expose the person to the risks associated with the disease.

Many vaccinations stimulate the immune system by exposing it to. Source for information on Immune Stimulation as a Vaccine. All vaccines work by priming the immune system against a potential infectious pathogen. Many challenges remain in expanding vaccine coverage to new pathogens however a struggle further hampered by a lack of understanding into many of the fundamental processes through which vaccines elicit robust immunity.
It also primes immune cells to. This type of infection however almost never causes illness but it does cause the immune system to produce T-lymphocytes and antibodies. As well immune stimulation shows promise as a means of obtaining an immune response to conditions such as cancer.
Vaccines contain weakened or killed versions of the germs that cause a disease. Vaccination teaches the body to recognize new diseases. In this way the immune system can more easily recognize and destroy any of these microorganisms in future encounters.
Regardless of whether the vaccine is made up of the antigen itself or the blueprint so that the body will produce the antigen this weakened version will not cause the disease in the. Recognize foreinfn antigens ans mark them for destruction. The use of vaccines has led to tremendous decreases in disease burdens across the world.
Thus vaccines prime our immune system to be better prepared for an infection if we are exposed to the pathogen again. Her finding is at the grim extreme of research on how well COVID-19 vaccines work in the many millions of people whose immune systems are suppressed by drugs or. The agent in a vaccine stimulates the bodys immune system to recognize the agent as foreign destroy it and remember it.
Vaccines are designed to generate immune memory In simplest terms vaccines are a way to give your immune system a sneak peek at a pathogen. A number of new vaccines. Vaccination stimulates the development of immunological memory and protects individuals from infectious diseases in the same way that natural infection does.
The immune system then keeps a memory of the disease so if a vaccinated person encounters the disease years later their immune system is ready to fight it off and prevent an infection from developing. These DNA strands would instruct the immune system to produce antigens for combating the pathogen all by itself. When a pathogen is encountered again the immune system ramps up production of these weapons preventing a virus or bacterium from taking hold for a.
An immune response is primarily due to the bodys white blood cells recognizing. Combined vaccines protect against multiple diseases by using a single product. Newer vaccines contain the blueprint for producing antigens rather than the antigen itself.
Immune stimulation as a vaccine Immune stimulation refers to the stimulation of the immune system by an external source. The stimulation can confer a protective effect against microorganisms. Still in experimental stages DNA vaccines would dispense with all unnecessary parts of a bacterium or virus and instead contain just an injection of a few parts of the pathogens DNA.
Exposure to an antigen stimulates an immune response which creates memory cells for that pathogen without causing the. The role of antibodies in the human is to. A direct indication that the white blood cells of the body are functioning would be.
Sometimes after getting a vaccine the. Vaccines typically contain part of a pathogen eg virus or bacterium and stimulate the production of antibodies against this pathogen. When a baby is born his or her immune system is ready to respond to.
Vaccines contain weakened or inactive parts of a particular organism antigen that triggers an immune response within the body. It stimulates the body to make antibodies against antigens of pathogens. Vaccines work by exposing the immune system to antigens from a specific pathogen tricking the body into thinking is has encountered the actual pathogen.
Modern vaccines use various methods to stimulate immune response including inactivated or modified pathogens or fragments of the target pathogen. Vaccines help develop immunity by imitating an infection. There are available vaccines against 23 diseases or pathogens that cause them.
In this review we cover recent advances in the field of innate immunity and vaccinology that offer new insights into the reasons some vaccines. Your immune system will still attack the harmless form of bacteria or virus from the vaccine and will produce antibodies to fight it off.
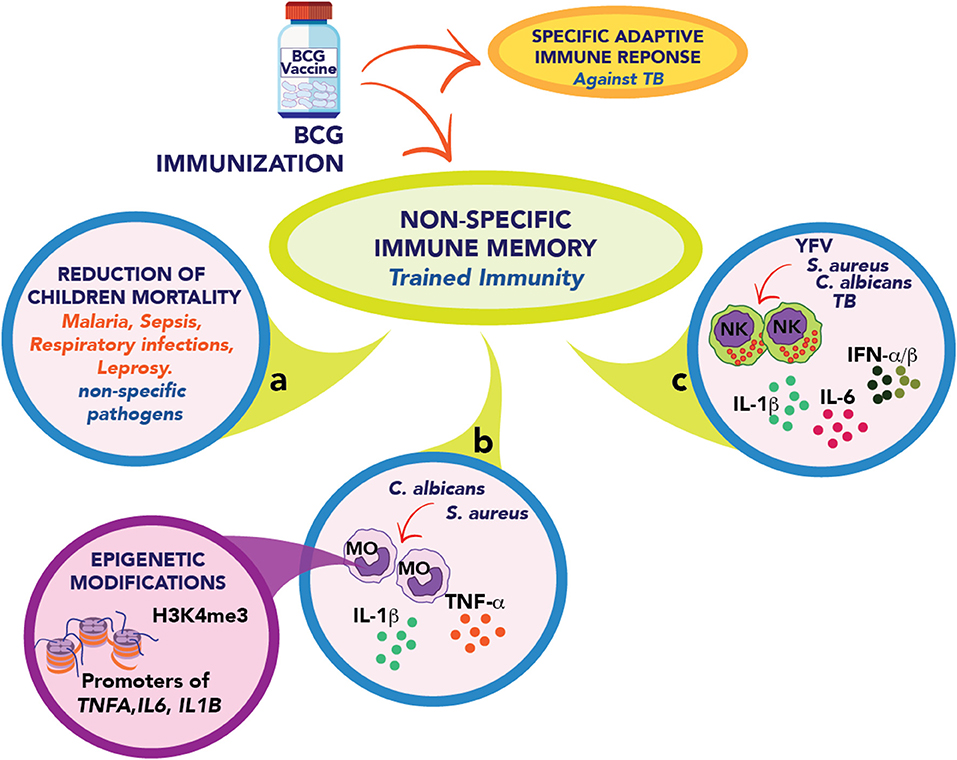 Frontiers Could Bcg Vaccination Induce Protective Trained Immunity For Sars Cov 2 Immunology
Frontiers Could Bcg Vaccination Induce Protective Trained Immunity For Sars Cov 2 Immunology
 Antiviral Immunity And Virus Vaccines Sciencedirect
Antiviral Immunity And Virus Vaccines Sciencedirect
 Module 1 How Vaccines Work Who Vaccine Safety Basics
Module 1 How Vaccines Work Who Vaccine Safety Basics
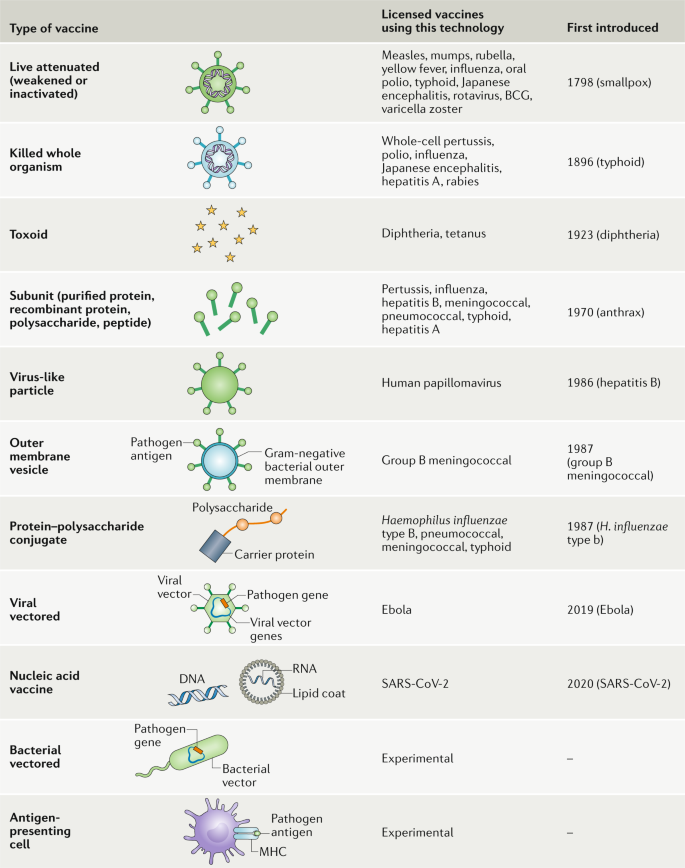 A Guide To Vaccinology From Basic Principles To New Developments Nature Reviews Immunology
A Guide To Vaccinology From Basic Principles To New Developments Nature Reviews Immunology
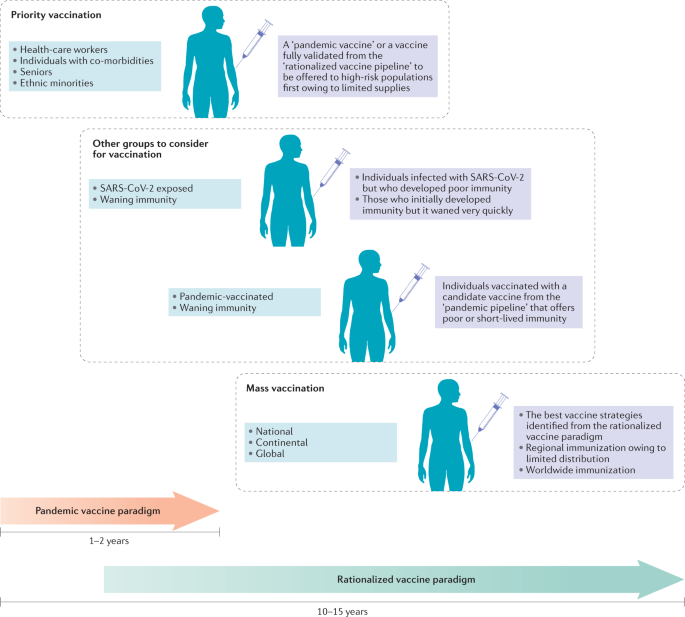 Immunological Considerations For Covid 19 Vaccine Strategies Nature Reviews Immunology
Immunological Considerations For Covid 19 Vaccine Strategies Nature Reviews Immunology
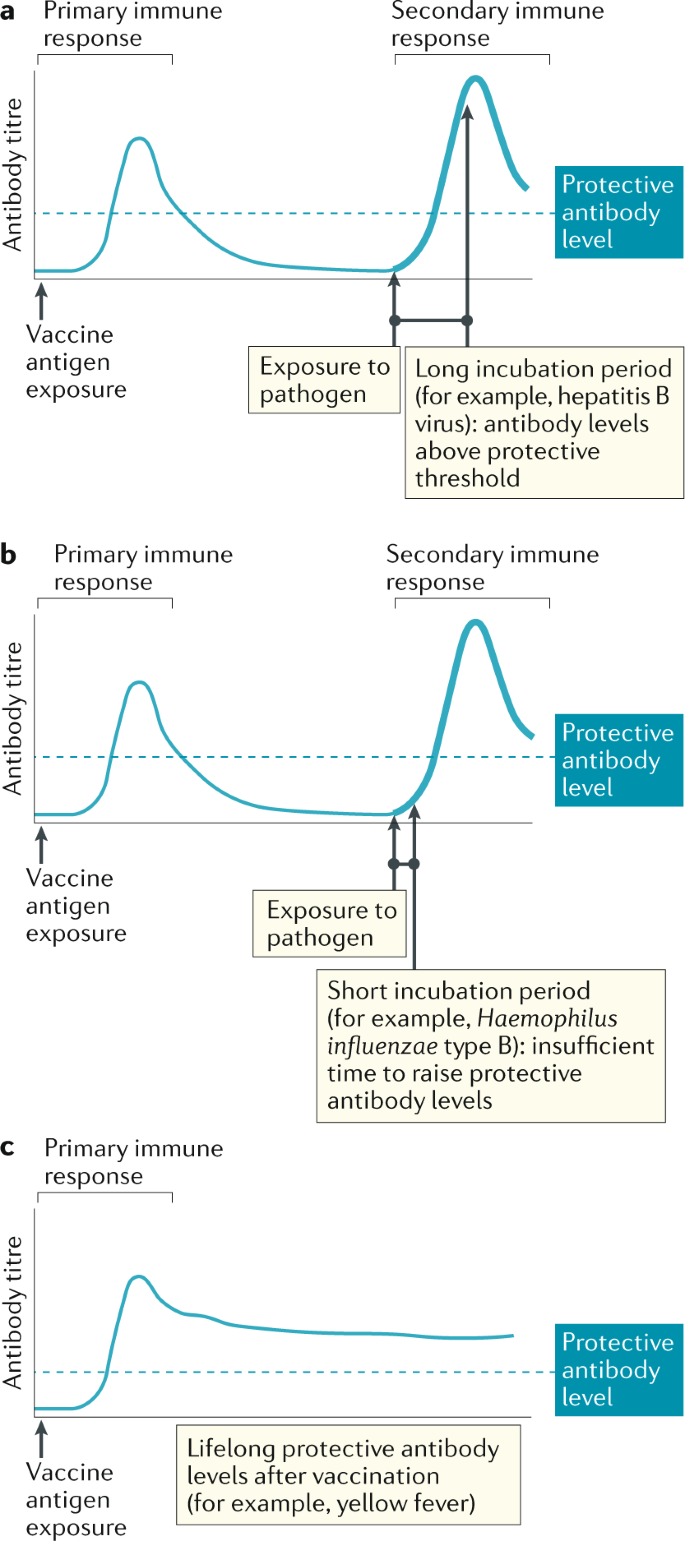 A Guide To Vaccinology From Basic Principles To New Developments Nature Reviews Immunology
A Guide To Vaccinology From Basic Principles To New Developments Nature Reviews Immunology
 Tuning Subunit Vaccines With Novel Tlr Triagonist Adjuvants To Generate Protective Immune Responses Against Coxiella Burnetii The Journal Of Immunology
Tuning Subunit Vaccines With Novel Tlr Triagonist Adjuvants To Generate Protective Immune Responses Against Coxiella Burnetii The Journal Of Immunology
 The Lymphatic System 5 Vaccinations And Immunological Memory Nursing Times
The Lymphatic System 5 Vaccinations And Immunological Memory Nursing Times

 What Does Immunogenicity Mean In The Context Of Covid 19 Vaccines
What Does Immunogenicity Mean In The Context Of Covid 19 Vaccines
Https Www Mdpi Com 1422 0067 21 18 6582 Pdf
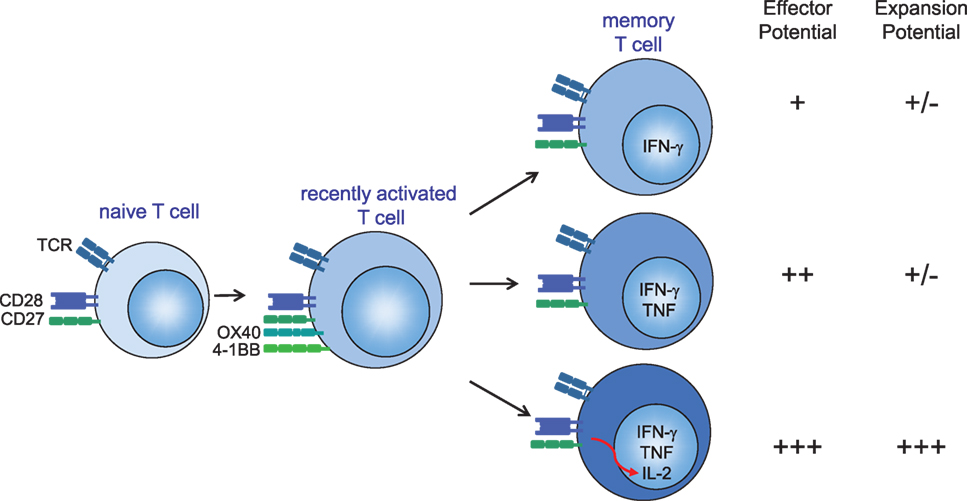 Frontiers Features Of Effective T Cell Inducing Vaccines Against Chronic Viral Infections Immunology
Frontiers Features Of Effective T Cell Inducing Vaccines Against Chronic Viral Infections Immunology
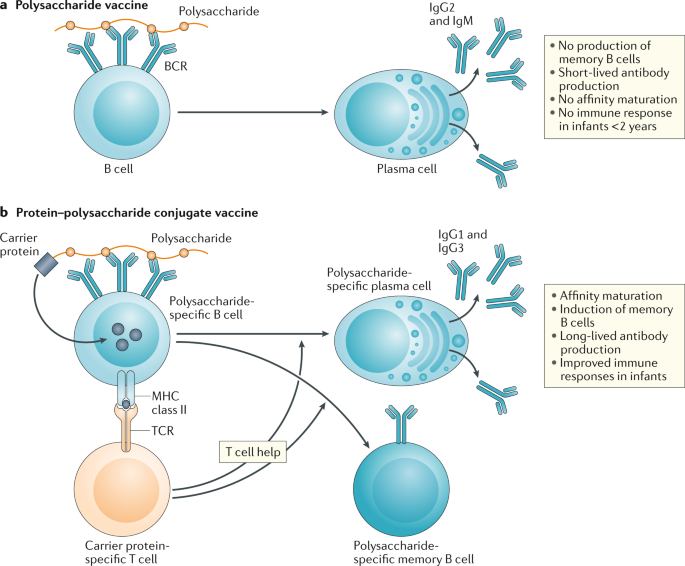 A Guide To Vaccinology From Basic Principles To New Developments Nature Reviews Immunology
A Guide To Vaccinology From Basic Principles To New Developments Nature Reviews Immunology
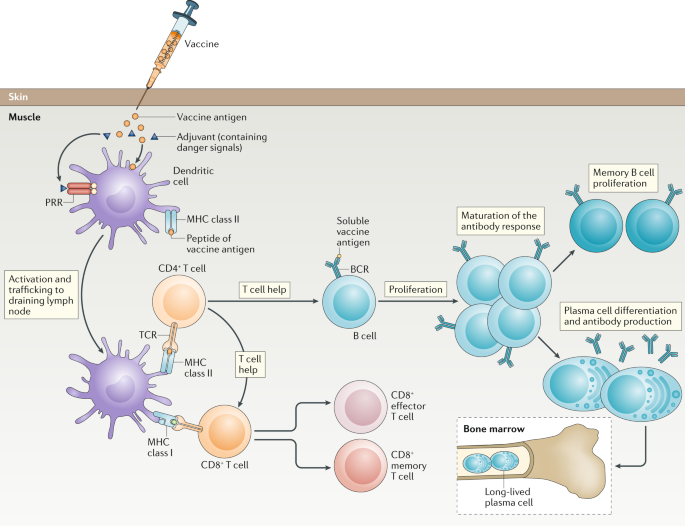 A Guide To Vaccinology From Basic Principles To New Developments Nature Reviews Immunology
A Guide To Vaccinology From Basic Principles To New Developments Nature Reviews Immunology

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.